A Helix And B Pleated Sheet
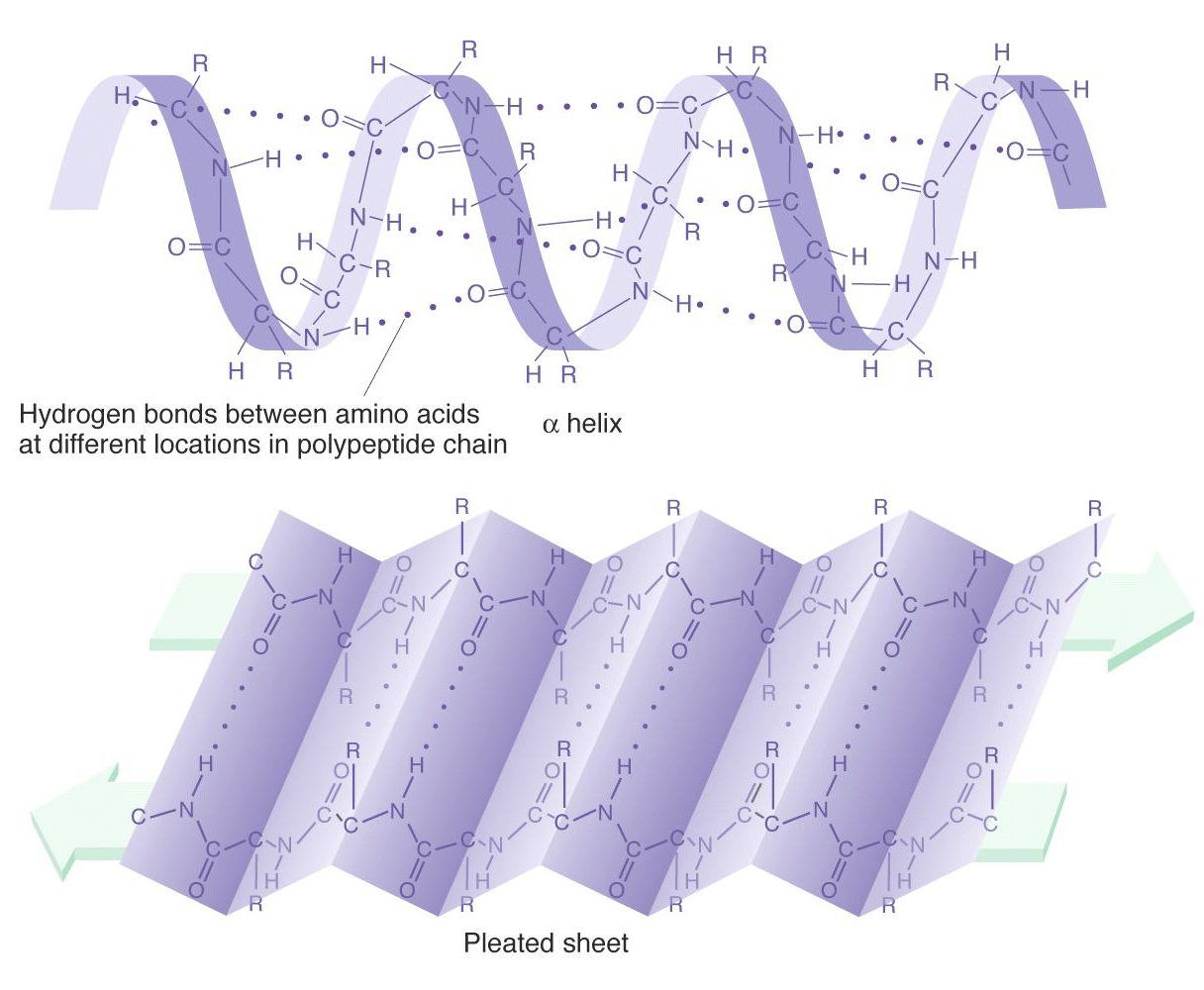
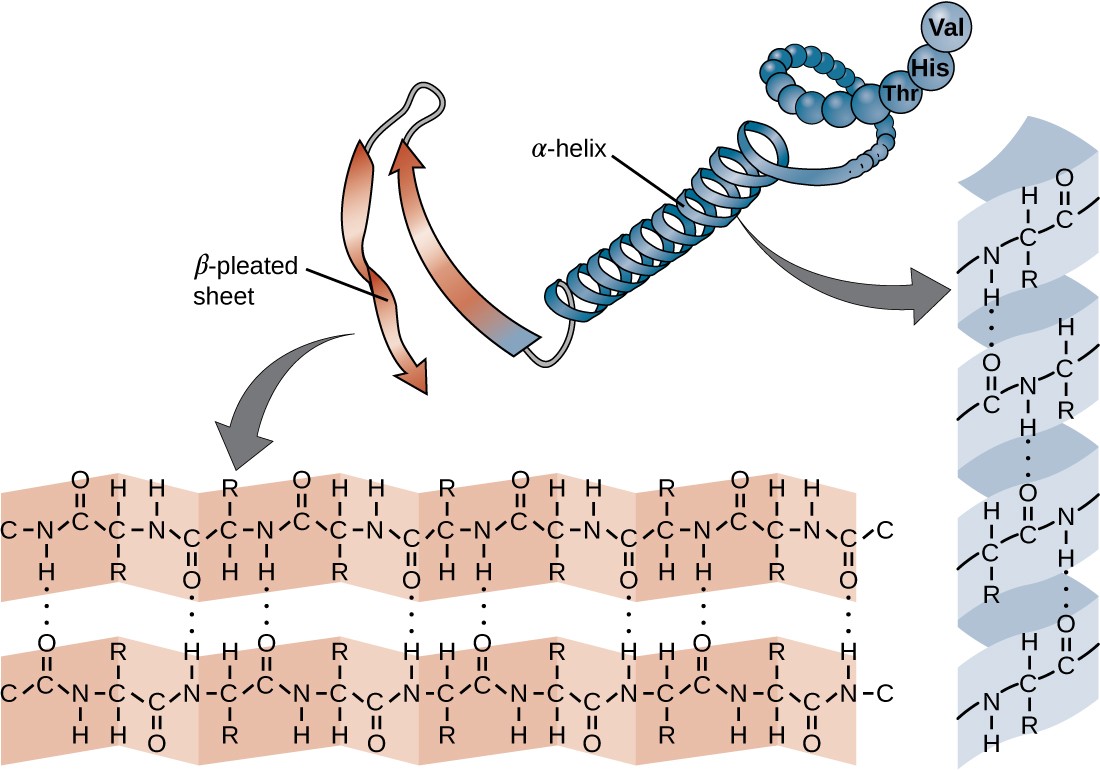
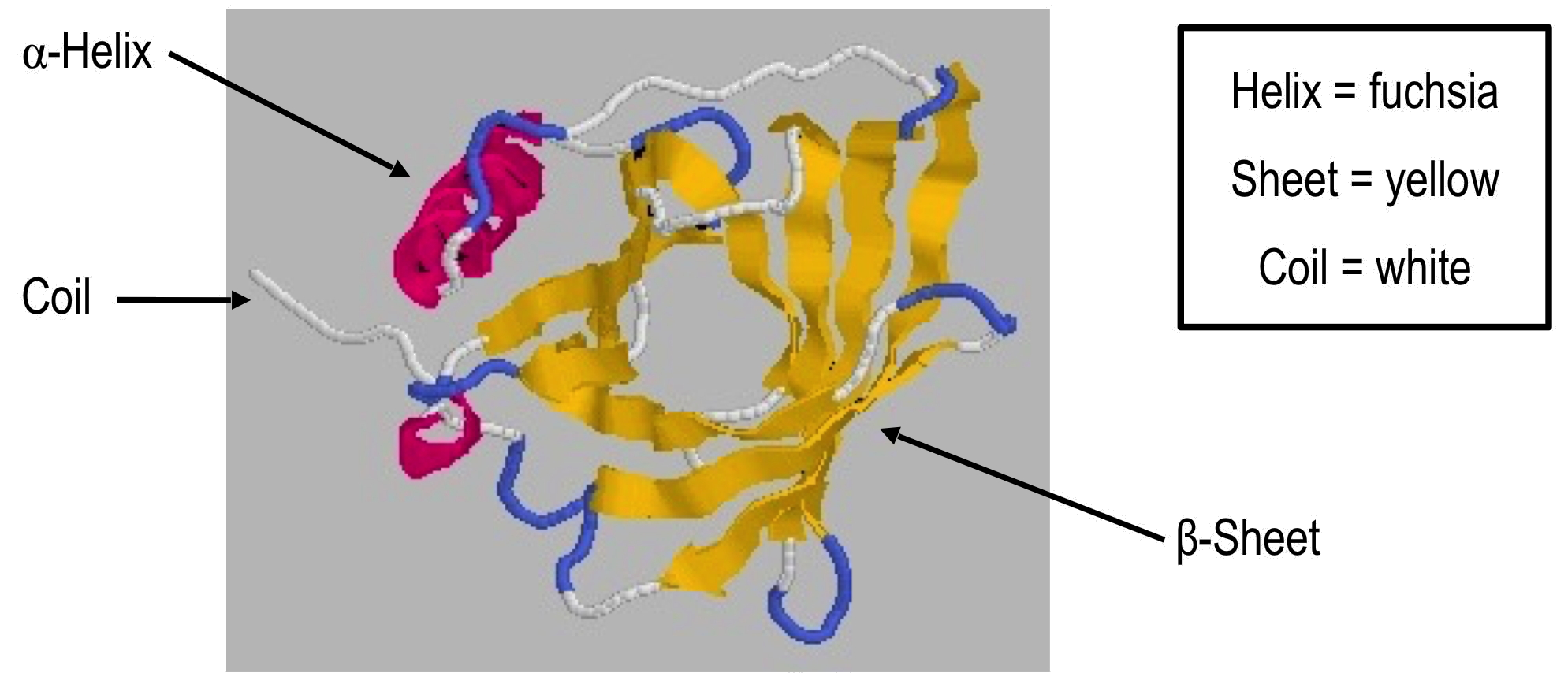
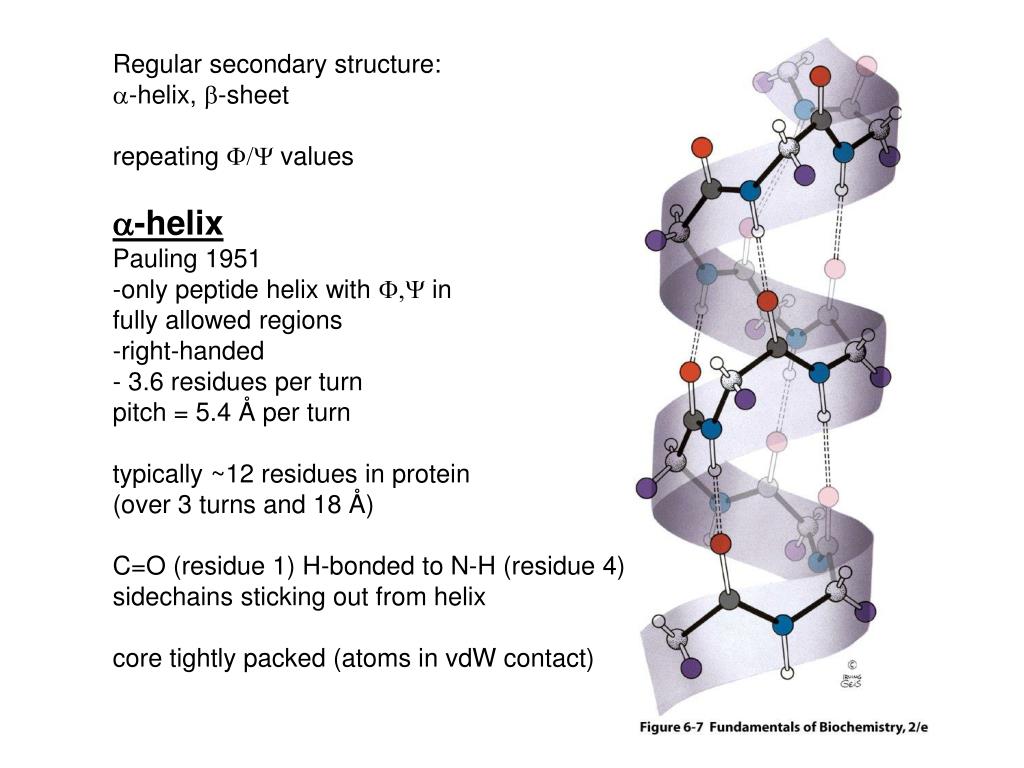
A Helix And B Pleated Sheet - The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are called. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet.
They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are called. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g.
They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are called. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet.
MGA2_0325
Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. The.
7.4 Proteins Microbiology 201
Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. This.
Secondary structures of keratin protein (beta pleated sheets and alpha
Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl.
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Coil; random coil
This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are called. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of.
Beta pleated sheet Secondary structure of protein YouTube
Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino.
PPT Regular secondary structure a helix, b sheet repeating F/Y
The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are called. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. This structure occurs when two (or more,.
Disulfide bonds Biochemistry3rst
They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the.
1. Secondary structure of protein, αhelix and βpleated sheet [118
They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are.
Alpha Helix vs Beta Pleated Sheet Diffzi
They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are called. Web the most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. Both structures are held in shape by.
difference between alpha helix and beta pleated sheet YouTube
They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g. The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular.
Web The Most Common Types Of Secondary Structures Are The Α Helix And The Β Pleated Sheet.
The other portions of the polymer backbone that are regular but not repetitive are called. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h of another. This structure occurs when two (or more, e.g.