Chapter 11 Lesson 3 Regulating The Cell Cycle Answer Key
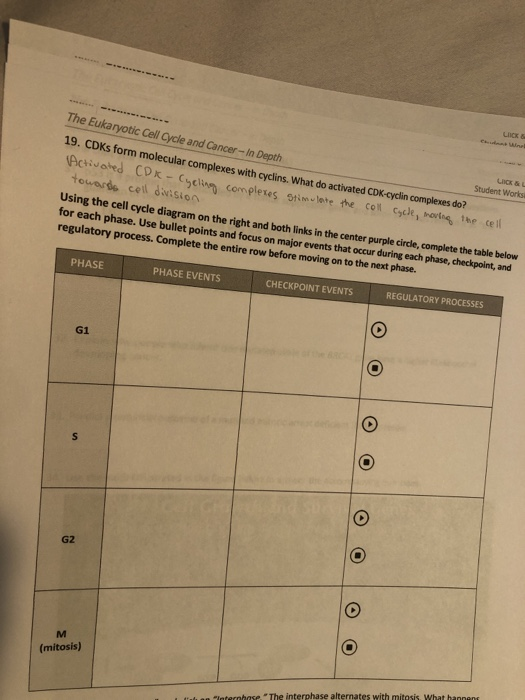
Chapter 11 Lesson 3 Regulating The Cell Cycle Answer Key - Label the diagram of the cell cycle below. Internal regulatory proteins proteins that act as checkpoints, allowing the cell cycle to proceed only when certain events have taken place. Cell cycle regulators (page 251) 3. Process of programmed cell death. Cell growth and cell division are. Lesson summary controls on cell division dozens of proteins regulate the cell cycle. They identified dozens of proteins that help to regulate the cell cycle. G _1 1 cyclins, g _1 1 /s cyclins, s cyclins, and m cyclins. The proteins signal the cell to either start or delay the next phase of the cycle. One of a family of proteins that regulates the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells.
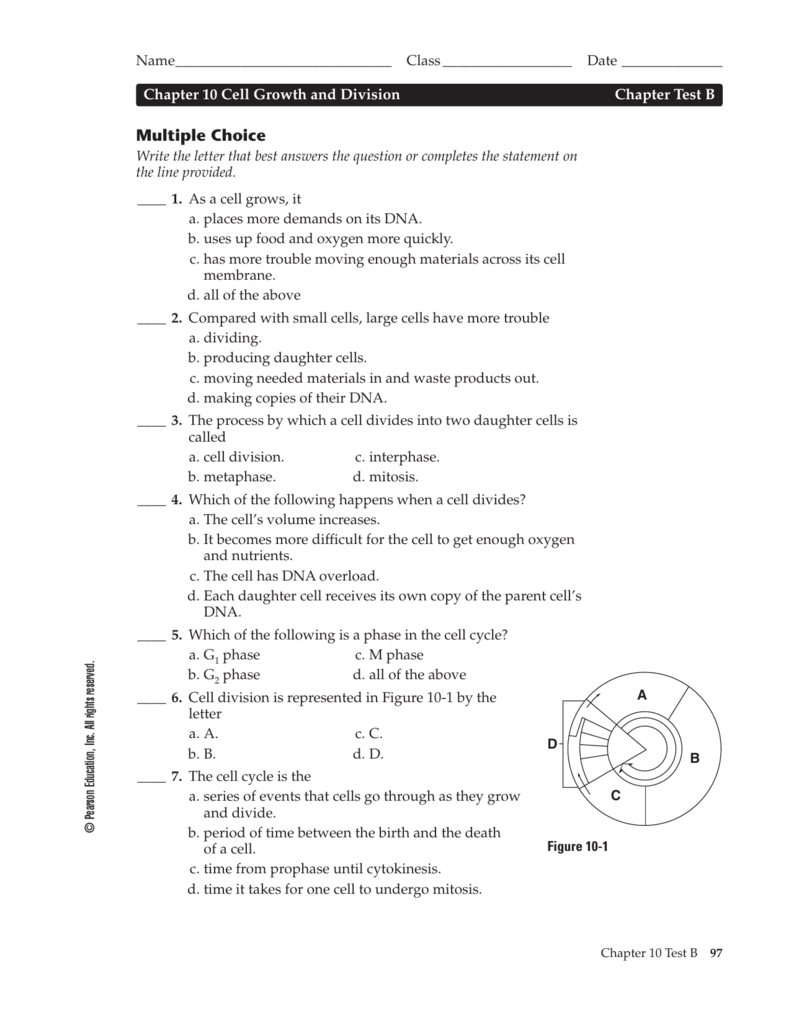
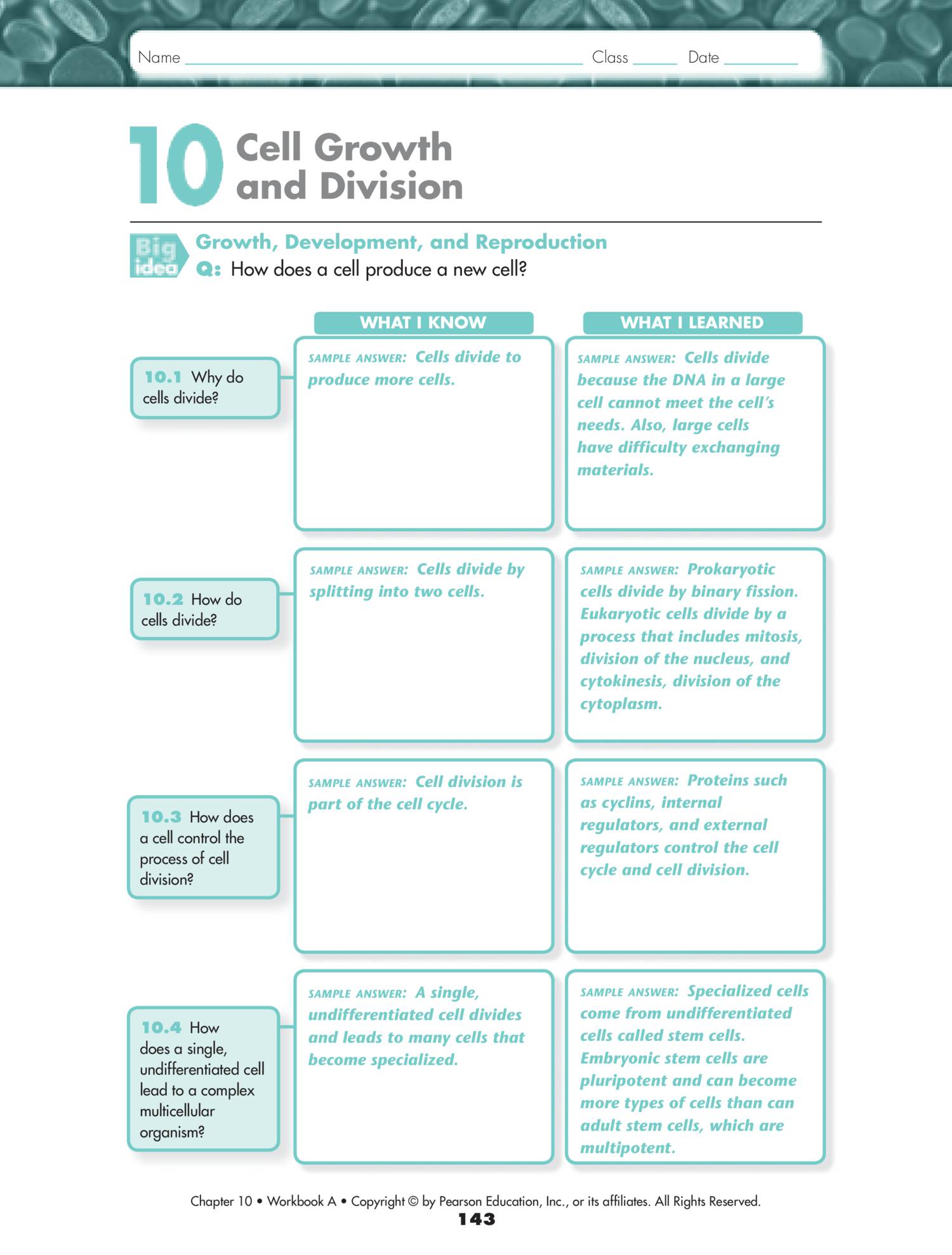
Cell growth & division biology a 8. • synthesize material for cell division 1) g 1 phase (growth phase 1) 2) s phase (synthesis phase) 3) g 2 phase (growth phase. The cell cycle is controlled by regulatory proteins both inside and outside the cell. Internal regulatory proteins proteins that act as checkpoints,. Web choose all answers that apply: Web cyclins are a family of proteins that regulate the timing of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells. Control of the cell cycle is necessary for a couple of reasons. Web the cell cycle is controlled by regulatory proteins at three key checkpoints in the cycle. Lesson summary controls on cell division dozens of proteins regulate the cell cycle. First, if the cell cycle were not regulated, cells could constantly undergo cell division.
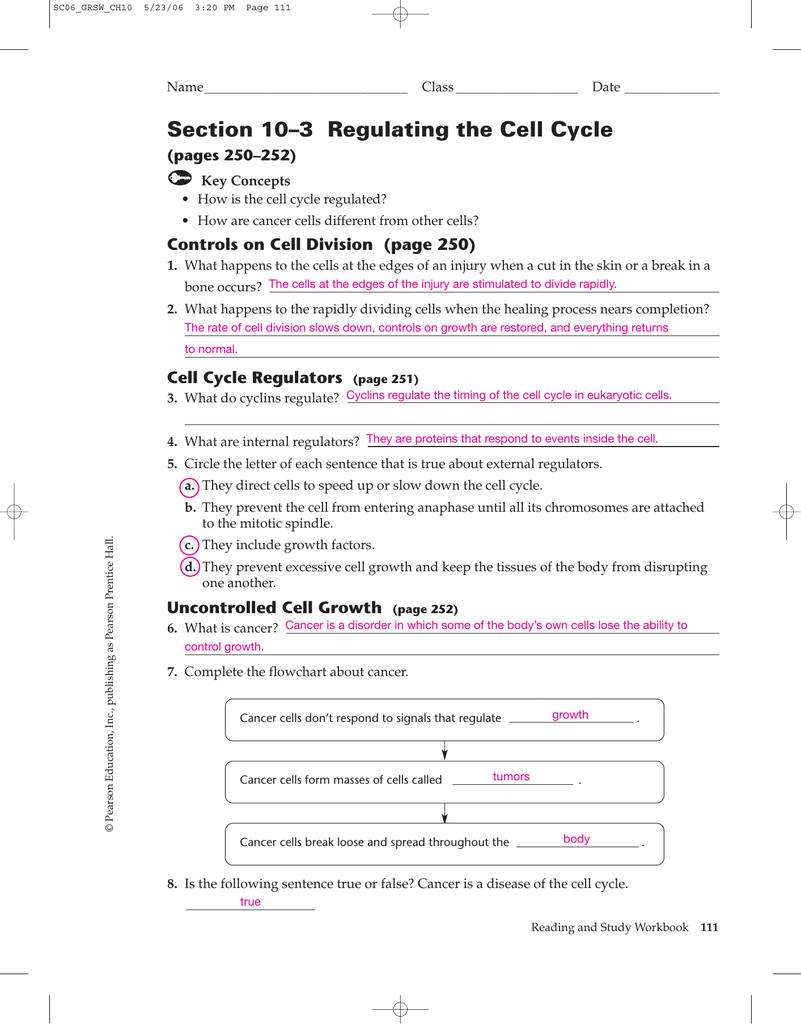
The chromosomes of the cell are not properly attached to spindle fibers. Cyclins regulate the timing of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells. 3 regulating the cell cycle reading tool make connections in the graphic organizer below, fill in each box with headings from this unit to help you understand the concepts. Explain how cancer cells are different from other cells. • synthesize material for cell division 1) g 1 phase (growth phase 1) 2) s phase (synthesis phase) 3) g 2 phase (growth phase. The cell cycle is controlled by ___ ___ both inside and outside the cell. Web choose all answers that apply: They are proteins that respond to events inside the cell… The cell's dna is damaged. 10.3 regulating the cell cycle lesson objectives describe how the cell cycle is regulated.
Chapter 10 3 Regulating The Cell Cycle Answer Key
The cell activity from one cell division to the next interphase (majority of time): Cancer is a disease that occurs when the cell cycle. Stimulate the growth and division of cells. • synthesize material for cell division 1) g 1 phase (growth phase 1) 2) s phase (synthesis phase) 3) g 2 phase (growth phase. Proteins called growth factors regulate.
53 Regulation Of The Cell Cycle Study Guide Answers Study Poster
Web [get] chapter 11 lesson 3 regulating the cell cycle answer key | free! Web cyclins are a group of related proteins, and there are four basic types found in humans and most other eukaryotes: 10.3 regulating the cell cycle lesson objectives describe how the cell cycle is regulated. The cell cycle is controlled by regulatory proteins both inside and.
Regulating the Cell Cycle Biology Quiz Quizizz
Web stimulate the growth and division of cells. What is the division of the cell nucleus called? How do cells know when it is time to divide? Cell growth and cell division are. The chromosomes of the cell are not properly attached to spindle fibers.
Cell Cycle Student Worksheet Answer Key / The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle And
Internal regulatory proteins proteins that act as checkpoints, allowing the cell cycle to proceed only when certain events have taken place. Lesson summary controls on cell division dozens of proteins regulate the cell cycle. Control of the cell cycle is necessary for a couple of reasons. 3 regulating the cell cycle reading tool make connections in the graphic organizer below,.
Chapter 10 3 Regulating The Cell Cycle Answer Key
One of a family of proteins that regulates the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells. Cyclins regulate the timing of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells. Control of the cell cycle is necessary for a couple of reasons. One of a family of proteins that regulates the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells. • synthesize material for cell division 1) g 1.
Chapter 10 3 Regulating The Cell Cycle Answer Key
One of a family of proteins that regulates the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells. They identified dozens of proteins that help to regulate the cell cycle. The chromosomes of the cell are not properly attached to spindle fibers. Internal regulatory proteins proteins that act as checkpoints, allowing the cell cycle to proceed only when certain events have taken place. The.
Ch_10_Cell_Growth_and_Division.pdf DocDroid
Cell growth and cell division are. Speed up or slow down the cell cycle. How do daughter cells split apart after the process named in question 11. Cyclins are proteins that regulate. First, if the cell cycle were not regulated, cells could constantly undergo cell division.
Regulating The Cell Cycle Worksheet —
They are proteins that respond to events inside the cell… This guided reading and review worksheet allows students to go over the section they just learned and answer. Web one of a family of proteins that regulates the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells. Web key question how is the cell cycle regulated? Internal regulatory proteins proteins that act as checkpoints,.
103 Regulating the Cell Cycle
Cyclins regulate the timing of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells. What happens during the cell cycle? Disorder in which some of. 3 regulating the cell cycle reading tool make connections in the graphic organizer below, fill in each box with headings from this unit to help you understand the concepts. One of a family of proteins that regulates the.
The Cell Cycle Is Controlled By Regulatory Proteins Both Inside And Outside The Cell.
Disorder in which some of. This guided reading and review worksheet allows students to go over the section they just learned and answer. They are proteins that respond to events inside the cell… Web cyclins are a family of proteins that regulate the timing of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells.
Cell Growth & Division Biology A 8.
Cell division speeds up when the healing process nears completion. What happens during the cell cycle? Cell cycle regulators (page 251) 3. 10.3 regulating the cell cycle lesson objectives describe how the cell cycle is regulated.
They Identified Dozens Of Proteins That Help To Regulate The Cell Cycle.
Process of programmed cell death. Web key question how is the cell cycle regulated? The chromosomes of the cell are not properly attached to spindle fibers. The cell activity from one cell division to the next interphase (majority of time):
One Of A Family Of Proteins That Regulates The Cell Cycle In Eukaryotic Cells.
How do daughter cells split apart after the process named in question 11. G _1 1 cyclins, g _1 1 /s cyclins, s cyclins, and m cyclins. Cyclins are proteins that regulate. Web stimulate the growth and division of cells.