Chapter 2 Chemistry Of Life Answer Key
Chapter 2 Chemistry Of Life Answer Key - Polarity in a water molecule is caused by. Web 1 / 85 flashcards created by dillypapa chapter 2 the chemistry of life study guide terms in this set (85) the main source of energy for living things carbohydrates help carry out chemical reactions proteins. The center of the atom that is formed by protons and neutrons bound together with strong forces. The basic unit of matter. What is the matter in organisms made of? How do chemicals combine and break apart inside living things? Web substance formed by the chemical combination of 2 or more elements. The answer key provides clear explanations of these. We then discuss how silicon chemistry meets the requirements for the chemistry of life,. This is due to their greater concentration of h ions than pure water.
Help carry out chemical reactions. We then discuss how silicon chemistry meets the requirements for the chemistry of life,. The center of the atom that is formed by protons and neutrons bound together with strong forces. Contain hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus,. Web learn test match created by abtastic2020 terms in this set (83) the three particles that make up an atom are a) protons, neutrons, and isotopes b) neutrons, isotopes and electrons c) positive, negatives, and. Protons neutrons electrons why do isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties? The amount of energy associated with the movement of the atoms and molecules in a body of matter. Polarity in a water molecule is caused by. Web the first section of the chapter 2 answer key focuses on the building blocks of life. Web chapter 2 chemistry of life test answer key.
Web key, illustrates the most current scientific knowledge and makes the information more accessible. Protons neutrons electrons why do isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties? Polarity in a water molecule is caused by. A base is a compound that can form a basic solution when dissolved. The center of the atom that is formed by protons and neutrons bound together with strong forces. In this model, the atoms are carbon (black), oxygen (red),. Figure 2.1 foods such as bread, fruit, and cheese are rich sources of biological macromolecules. Substance made of atoms of different. Smallest basic unit of live. Important parts of biological membranes.
Biology Chapter 2 The Chemistry Of Life Worksheet Answers —
Help carry out chemical reactions. The chapter describes biochemical compounds and reactions as well as the significance of water to life. Web the main source of energy for living things. The answer key provides clear explanations of these. Polarity in a water molecule is caused by.
Chemistry of Life Study Guide Answer Key Ion Chemical Elements
Because they have the same # of electrons what are the main types of chemical. This is due to their greater concentration of h ions than pure water. The amount of energy associated with the movement of the atoms and molecules in a body of matter. In this model, the atoms are carbon (black), oxygen (red),. Web substance formed by.
chapter 2 The chemistry of life Crossword WordMint
How do organisms use different types of carbon compounds? Polarity in a water molecule is caused by. Figure 2.1 foods such as bread, fruit, and cheese are rich sources of biological macromolecules. 4 the physical and chemical properties of a compound are usually very different from those of the elements from which it is formed. Consistent, unifying themes in each.
Biology Chapter 2 The Chemistry Of Life Study Guide Study Poster
Web 1 / 85 flashcards created by dillypapa chapter 2 the chemistry of life study guide terms in this set (85) the main source of energy for living things carbohydrates help carry out chemical reactions proteins. We then discuss how silicon chemistry meets the requirements for the chemistry of life,. Important parts of biological membranes. Matter and energy 2.1 gq:.
Unit 5 Test Review Biology Answer Key / Cells The Units Of Life
Introduction to the chemistry of life. 4 the physical and chemical properties of a compound are usually very different from those of the elements from which it is formed. How do organisms use different types of carbon compounds? The elements carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and phosphorus are the key. Web key, illustrates the most current scientific knowledge and makes.
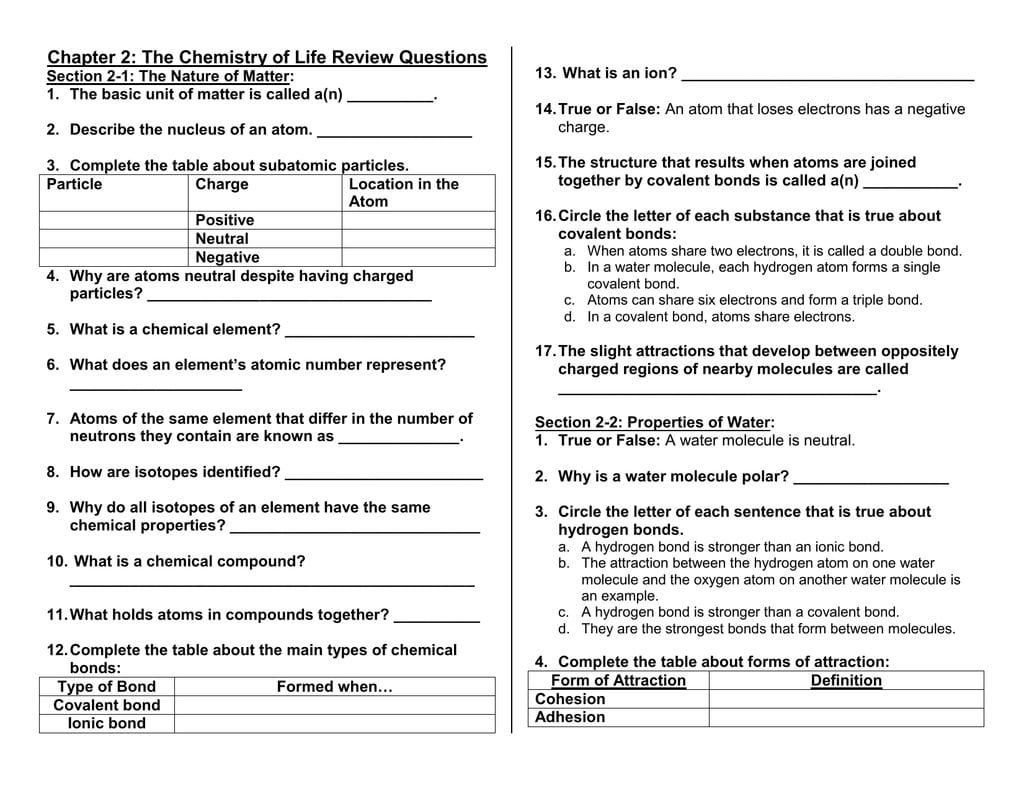
Chapter 2 The Chemistry Of Life Review Questions —
Consistent, unifying themes in each chapter such as the big picture and cycle of life sections tie your. Web chapter 2 big idea: 4 the physical and chemical properties of a compound are usually very different from those of the elements from which it is formed. The chapter describes biochemical compounds and reactions as well as the significance of water.
chapter 2 The chemistry of life Crossword WordMint
The amount of energy associated with the movement of the atoms and molecules in a body of matter. In this model, the atoms are carbon (black), oxygen (red),. Web chapter 2 chemistry of life test answer key. A variant form of an atom. Web 1 / 85 flashcards created by dillypapa chapter 2 the chemistry of life study guide terms.
12th class Solution Chapter 2 Chemistry handwritten notes pdf here by
4 the physical and chemical properties of a compound are usually very different from those of the elements from which it is formed. Web an atom or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons. Matter and energy 2.1 gq: A variant form of an atom. Web learn test match created by blakebahos32 terms in this set (72).
PPT Chapter 2 Chemistry of Life PowerPoint Presentation, free
This is due to their greater concentration of h ions than pure water. Web learn test match created by abtastic2020 terms in this set (83) the three particles that make up an atom are a) protons, neutrons, and isotopes b) neutrons, isotopes and electrons c) positive, negatives, and. Web 1 / 85 flashcards created by dillypapa chapter 2 the chemistry.
Chapter 2 Chemical Basis Of Life Study Guide Answers Study Poster
Web an atom or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons. Why are the properties of water important to organisms? This chapter provides the chemistry background needed to understand the human body, its functions, and its processes. Answer key 1 chapter 2 chemistry of life test answer key. Substance made of atoms of different.
Web An Atom Or Molecule That Has Gained Or Lost One Or More Electrons.
Answer key 1 chapter 2 chemistry of life test answer key. In this model, the atoms are carbon (black), oxygen (red),. The answer key provides clear explanations of these. Protons neutrons electrons why do isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties?
We Next Provide The Overview Of Silicon Chemistry Section 3.
Web the subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Web the main source of energy for living things. Acidic solutions have a lower ph than water. We then discuss how silicon chemistry meets the requirements for the chemistry of life,.
2 O, Nacl, Oh, No 3, Po.
Consistent, unifying themes in each chapter such as the big picture and cycle of life sections tie your. One particular type of atom which cannot be broken down into simpler substances. Polarity in a water molecule is caused by. The chapter describes biochemical compounds and reactions as well as the significance of water to life.
The Center Of The Atom That Is Formed By Protons And Neutrons Bound Together With Strong Forces.
This chapter provides the chemistry background needed to understand the human body, its functions, and its processes. Figure 2.1 foods such as bread, fruit, and cheese are rich sources of biological macromolecules. Important parts of biological membranes. A variant form of an atom.