Complex Numbers Polar Form
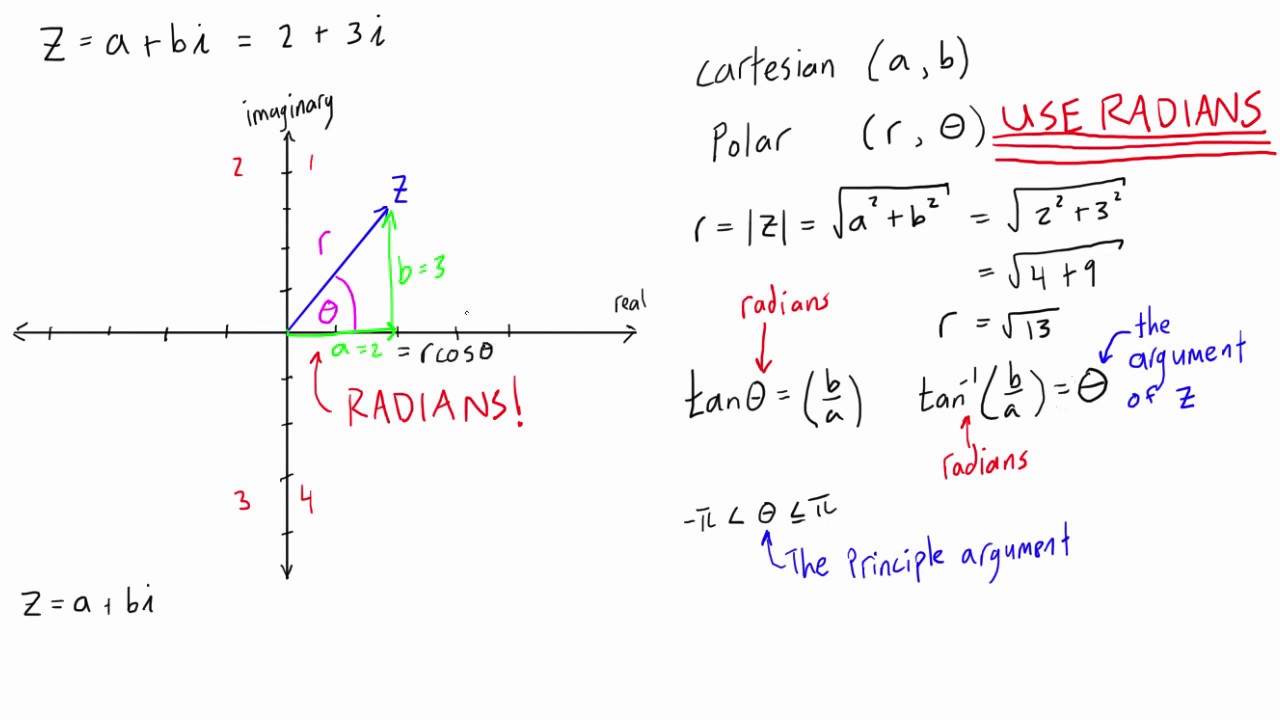
Complex Numbers Polar Form - Web the equation of polar form of a complex number z = x+iy is: Plotting a complex number a + bi is similar to plotting a real number,. Converting rectangular form into polar form. R=|z|=√(x 2 +y 2) x=r cosθ. Note first that (a r)2 + (b r)2 = a2 + b2 r2 = 1 and so (a r, b r) is a point on the unit circle. Finding the absolute value of a complex number. Web precalculus8.5polar form of complex numbers close menu contentscontents highlights print table of contents preface 1functions introduction to functions 1.1functions and function notation 1.2domain and range 1.3rates of change and behavior of graphs 1.4composition of functions 1.5transformation of functions 1.6absolute value functions Let us see some examples of conversion of the rectangular form of complex numbers into polar form. Web the polar form is the focus of this section. The polar form of complex numbers plotting complex numbers in the complex plane.
The polar form of complex numbers plotting complex numbers in the complex plane. Recall that r is the modulus of z. Web review the polar form of complex numbers, and use it to multiply, divide, and find powers of complex numbers. Converting rectangular form into polar form. Since we saw that the cartesian coordinates are (a, b), then: Plotting a complex number a + bi is similar to plotting a real number,. Finding the absolute value of a complex number. \goldd {\text {absolute value}} absolute value (the distance of the number from the origin in the complex plane) and \purplec {\text {angle}} angle (the angle that. The first step toward working with a complex number in polar form is to. Polar form of complex numbers plotting complex numbers in the complex plane.
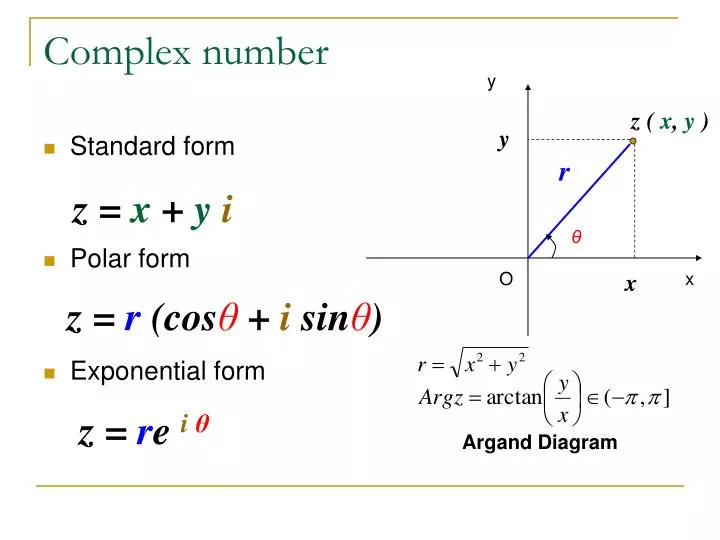
Web the polar form is the focus of this section. Web the polar coordinates of a a complex number is in the form (r, θ). Finding the absolute value of a complex number. Converting rectangular form into polar form. Web precalculus8.5polar form of complex numbers close menu contentscontents highlights print table of contents preface 1functions introduction to functions 1.1functions and function notation 1.2domain and range 1.3rates of change and behavior of graphs 1.4composition of functions 1.5transformation of functions 1.6absolute value functions R ( cos θ + i sin θ ) \goldd r(\cos\purplec\theta+i\sin\purplec\theta) r ( cos θ + i sin θ ) start color #e07d10, r, end color #e07d10, left parenthesis, cosine, start color #aa87ff, theta, end color #. Note first that (a r)2 + (b r)2 = a2 + b2 r2 = 1 and so (a r, b r) is a point on the unit circle. The first step toward working with a complex number in polar form is to. The polar form of a complex number z = a + b i is z = r ( cos θ + i sin θ) , where r = | z | = a 2 + b 2 , a = r cos θ and b = r sin θ , and θ = tan − 1 ( b a) for a > 0 and θ = tan − 1 ( b a) + π or θ = tan − 1 ( b a) + 180 ° for a < 0. Plotting a complex number a + bi is similar to plotting a real number,.
Polar Form of Complex Number Meaning, Formula, Examples
Let us see some examples of conversion of the rectangular form of complex numbers into polar form. Since we saw that the cartesian coordinates are (a, b), then: Find more mathematics widgets in wolfram|alpha. The first step toward working with a complex number in polar form is to. A = r*cos(θ) b = r*sin(θ) and since the rectangular form of.
Polar Form of Complex Number Meaning, Formula, Examples
Find more mathematics widgets in wolfram|alpha. Finding the absolute value of a complex number. Note first that (a r)2 + (b r)2 = a2 + b2 r2 = 1 and so (a r, b r) is a point on the unit circle. Plotting a complex number a + bi is similar to plotting a real number,. Converting rectangular form into.
Writing a Complex Number in Polar Form YouTube
Finding the absolute value of a complex number. The polar form of a complex number z = a + b i is z = r ( cos θ + i sin θ) , where r = | z | = a 2 + b 2 , a = r cos θ and b = r sin θ , and θ.
Complex Number Polar Form / Lesson 2 Polar Form of Complex Numbers
Plotting a complex number a + bi is similar to plotting a real number,. Let us see some examples of conversion of the rectangular form of complex numbers into polar form. R ( cos θ + i sin θ ) \goldd r(\cos\purplec\theta+i\sin\purplec\theta) r ( cos θ + i sin θ ) start color #e07d10, r, end color #e07d10,.
Complex Number Polar Form slidesharedocs
Finding the absolute value of a complex number. Plotting a complex number a + bi is similar to plotting a real number,. Let us see some examples of conversion of the rectangular form of complex numbers into polar form. Web the equation of polar form of a complex number z = x+iy is: Web get the free convert complex numbers.
Polar form of complex numbers How to calculate? YouTube
Let us see some examples of conversion of the rectangular form of complex numbers into polar form. R=|z|=√(x 2 +y 2) x=r cosθ. Plotting a complex number a + bi is similar to plotting a real number,. Plotting a complex number a + bi is similar to plotting a real number,. If you want to go from polar coordinates to.
How to write a complex number in polar form YouTube
The polar form of a complex number z = a + b i is z = r ( cos θ + i sin θ) , where r = | z | = a 2 + b 2 , a = r cos θ and b = r sin θ , and θ = tan − 1 ( b a) for.
Complex Number Polar Form / Lesson 2 Polar Form of Complex Numbers
Web the polar form is the focus of this section. R=|z|=√(x 2 +y 2) x=r cosθ. \goldd {\text {absolute value}} absolute value (the distance of the number from the origin in the complex plane) and \purplec {\text {angle}} angle (the angle that. Since we saw that the cartesian coordinates are (a, b), then: Finding the absolute value of a complex.
Polar form of Complex Numbers (Formula and Equation)
Web the equation of polar form of a complex number z = x+iy is: The polar form of complex numbers plotting complex numbers in the complex plane. Let us see some examples of conversion of the rectangular form of complex numbers into polar form. Web the polar coordinates of a a complex number is in the form (r, θ). The.
Complex Number Polar Form / Lesson 2 Polar Form of Complex Numbers
Web precalculus8.5polar form of complex numbers close menu contentscontents highlights print table of contents preface 1functions introduction to functions 1.1functions and function notation 1.2domain and range 1.3rates of change and behavior of graphs 1.4composition of functions 1.5transformation of functions 1.6absolute value functions Suppose z = a + bi is a complex number, and let r = √a2 + b2 =.
Web The Polar Form Is The Focus Of This Section.
Plotting a complex number a + bi is similar to plotting a real number,. Since we saw that the cartesian coordinates are (a, b), then: Let us see some examples of conversion of the rectangular form of complex numbers into polar form. Plotting a complex number a + bi is similar to plotting a real number,.
Web Precalculus8.5Polar Form Of Complex Numbers Close Menu Contentscontents Highlights Print Table Of Contents Preface 1Functions Introduction To Functions 1.1Functions And Function Notation 1.2Domain And Range 1.3Rates Of Change And Behavior Of Graphs 1.4Composition Of Functions 1.5Transformation Of Functions 1.6Absolute Value Functions
Suppose z = a + bi is a complex number, and let r = √a2 + b2 = | z |. R ( cos θ + i sin θ ) \goldd r(\cos\purplec\theta+i\sin\purplec\theta) r ( cos θ + i sin θ ) start color #e07d10, r, end color #e07d10, left parenthesis, cosine, start color #aa87ff, theta, end color #. Note first that (a r)2 + (b r)2 = a2 + b2 r2 = 1 and so (a r, b r) is a point on the unit circle. R=|z|=√(x 2 +y 2) x=r cosθ.
Web The Polar Coordinates Of A A Complex Number Is In The Form (R, Θ).
If you want to go from polar coordinates to cartesian coordinates, that is just: Converting rectangular form into polar form. Find more mathematics widgets in wolfram|alpha. Polar form of complex numbers plotting complex numbers in the complex plane.
Web Polar Form Emphasizes The Graphical Attributes Of Complex Numbers:
Finding the absolute value of a complex number. A = r*cos(θ) b = r*sin(θ) and since the rectangular form of a complex number is a + bi, just replace the letters: Web the equation of polar form of a complex number z = x+iy is: The polar form of a complex number z = a + b i is z = r ( cos θ + i sin θ) , where r = | z | = a 2 + b 2 , a = r cos θ and b = r sin θ , and θ = tan − 1 ( b a) for a > 0 and θ = tan − 1 ( b a) + π or θ = tan − 1 ( b a) + 180 ° for a < 0.