Lipids Simplest Form
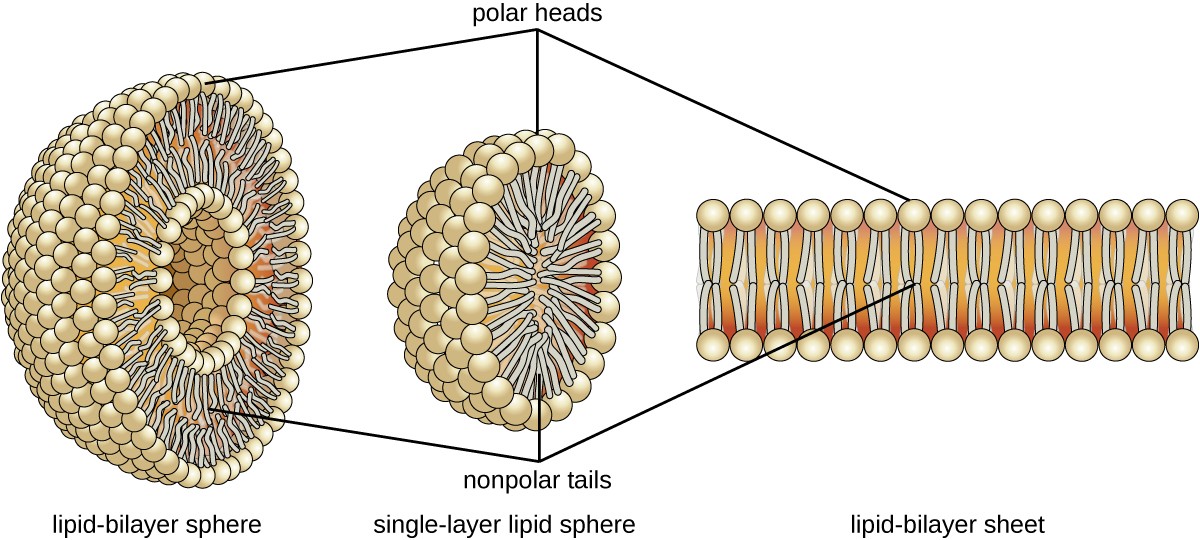
Lipids Simplest Form - Web the simplest of these structures are micelles, spherical assemblies containing a hydrophobic interior of phospholipid tails and an outer surface of polar head groups. They’re part of your cell membranes and help control what goes in and out of your cells. Hydrophilic (polar) phosphate heads 2. Monosaccharides are simple sugars and are the simplest form of. Web simple lipids are lipids that are formed when fatty acids react with alcohols. These lipids belong to a heterogeneous class of predominantly nonpolar compounds,. Web lipid categorized into fatty acids and steroids. Study examples of the classes of lipids, examine the structure and forms of lipids, and discover why lipids are important for. Web monomers and polymers of lipids? Web no a monosaccharide is not a lipid.
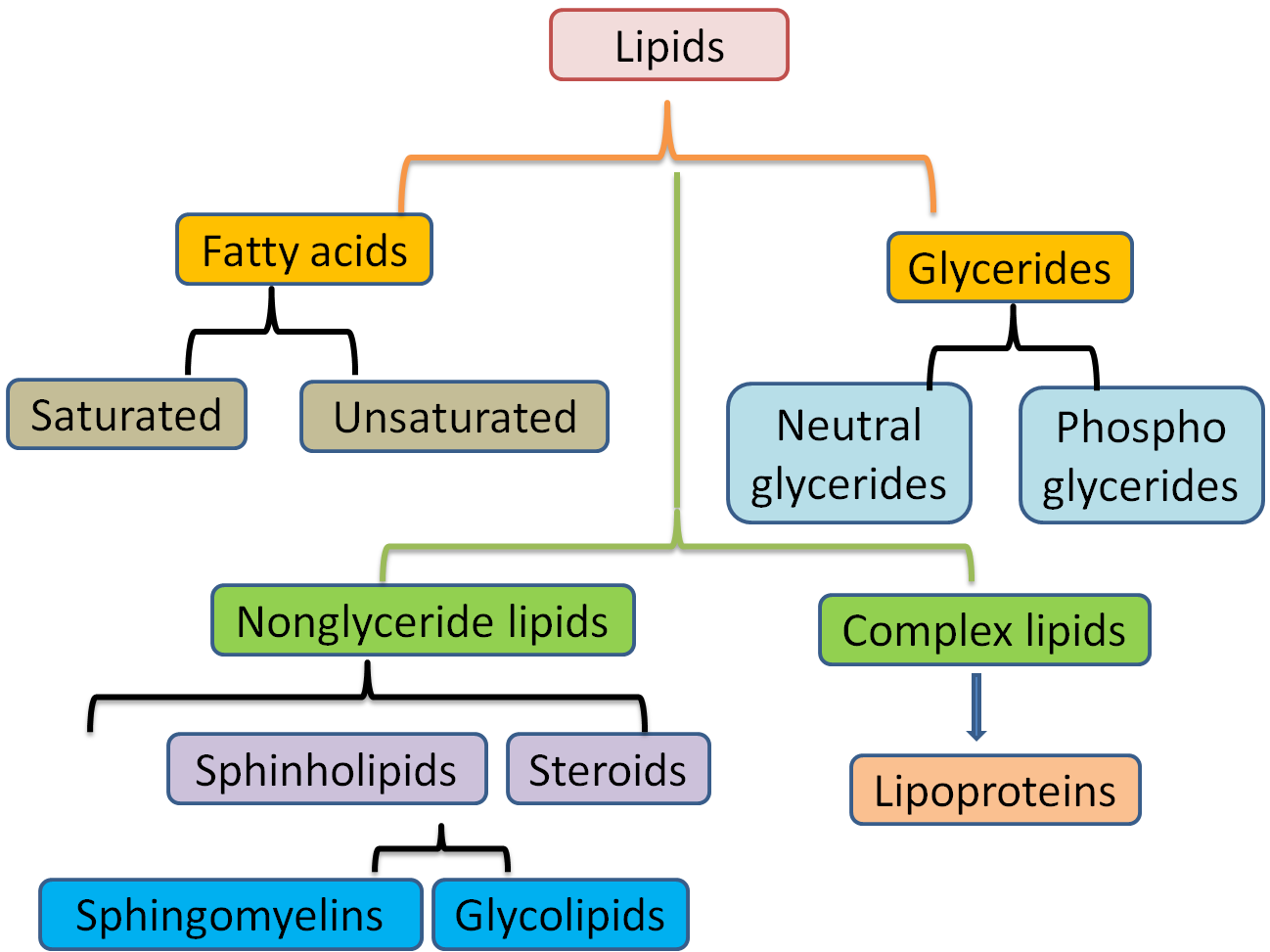
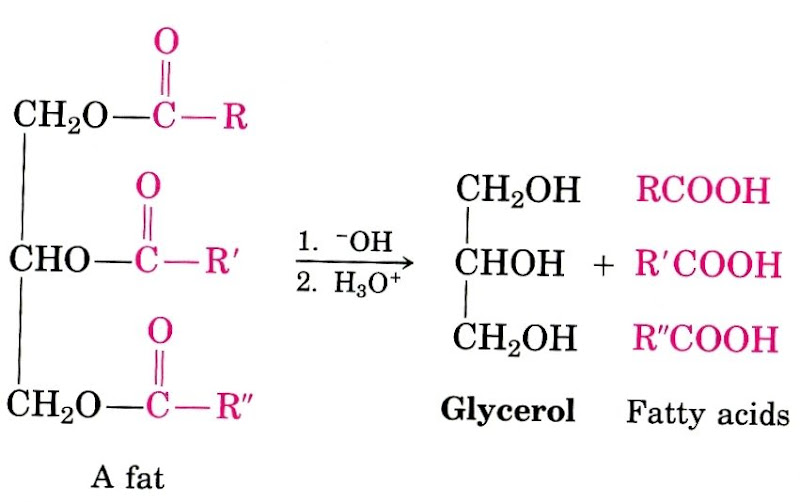
Web lipid categorized into fatty acids and steroids. Monosaccharides are simple sugars and are the simplest form of. Web simple lipids are lipids that are formed when fatty acids react with alcohols. A lipid can be either a fat, steroids, cholesterol, or waxes. The simplest lipid mixture shown to induce domain (“raft”) formation consists of cholesterol and both a saturated and unsaturated species of phospholipid. Triglyceride is the simplest lipid composed of three fatty acids that are connected with ester. Web lipids can form bonds to proteins and carbohydrates forming lipoproteins and lipopolysaccharides. Web 7.2.3 lipid 7.2.3.1 triglyceride. Web learn about types of lipids. They’re part of your cell membranes and help control what goes in and out of your cells.
Web what are the simplest forms (monomers) of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids? Web no a monosaccharide is not a lipid. So we cannot speak of monomers and polymers of lipids.lipids are. Web lipid categorized into fatty acids and steroids. Web monomers and polymers of lipids? Monosaccharides are simple sugars and are the simplest form of. In contrast, complex lipids contain at least one. Examples of simple lipids include solid fats, liquid fats (or oils), and waxes. Web learn about types of lipids. Web the simplest of these structures are micelles, spherical assemblies containing a hydrophobic interior of phospholipid tails and an outer surface of polar head groups.
Lipids Microbiology
Study examples of the classes of lipids, examine the structure and forms of lipids, and discover why lipids are important for. Web what are the simplest forms (monomers) of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids? Web learn about types of lipids. Web simple lipids are lipids that are formed when fatty acids react with alcohols. Web monomers and polymers of.
What Are Lipids?
Hydrophilic (polar) phosphate heads 2. There are eight categories of lipids defined by the lipid maps. Web monomers and polymers of lipids? Web lipid categorized into fatty acids and steroids. Web triglycerides are classified as simple lipids because they are formed from just two types of compounds:
Lipids
So we cannot speak of monomers and polymers of lipids.lipids are. Web lipid categorized into fatty acids and steroids. Examples of simple lipids include solid fats, liquid fats (or oils), and waxes. Web simple lipids are lipids that are formed when fatty acids react with alcohols. Web the simplest of these structures are micelles, spherical assemblies containing a hydrophobic interior.
Lipids
Monosaccharides are simple sugars and are the simplest form of. Web the simplest of these structures are micelles, spherical assemblies containing a hydrophobic interior of phospholipid tails and an outer surface of polar head groups. So we cannot speak of monomers and polymers of lipids.lipids are. Web learn about types of lipids. Study examples of the classes of lipids, examine.
Lipids
Web lipid anabolism describes the production of complex lipid molecules from simple ones using energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (the energy source. In contrast, complex lipids contain at least one. A lipid can be either a fat, steroids, cholesterol, or waxes. Examples of simple lipids include solid fats, liquid fats (or oils), and waxes. Lipids are not polymers.
What Are Lipids? — Structure & Function Expii
Lipids are fatty compounds that perform a variety of functions in your body. Web what are the simplest forms (monomers) of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids? Lipids are not polymers but are macromolecules. Web lipid anabolism describes the production of complex lipid molecules from simple ones using energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (the energy source. Monosaccharides are.
Lipid Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Web triglycerides are classified as simple lipids because they are formed from just two types of compounds: Web lipid anabolism describes the production of complex lipid molecules from simple ones using energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (the energy source. Lipids are not polymers but are macromolecules. Web the simplest of these structures are micelles, spherical assemblies containing a.
2.8 Lipids Biology LibreTexts
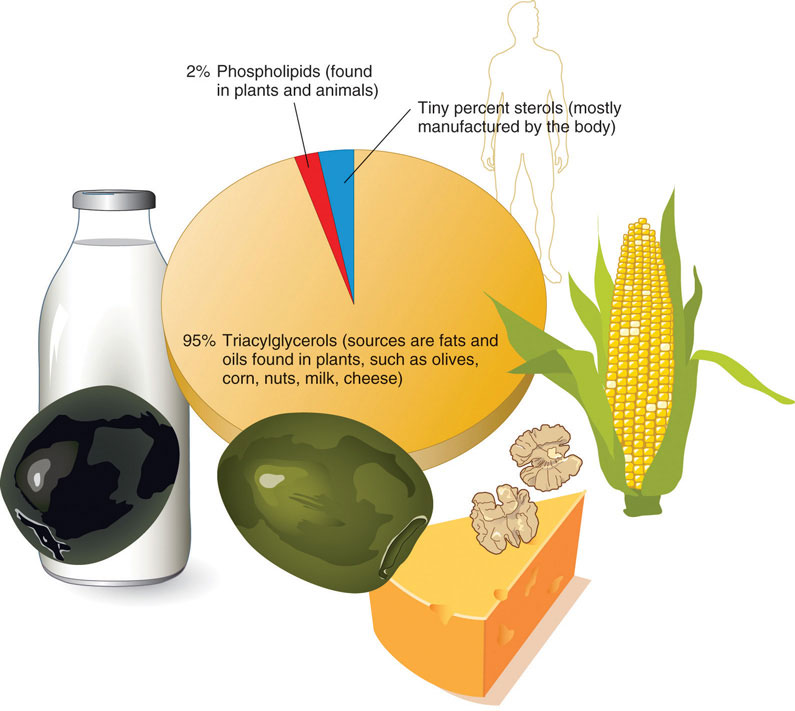
They’re part of your cell membranes and help control what goes in and out of your cells. Web a simple lipid is a fatty acid ester of different alcohols and carries no other substance. Triglyceride is the simplest lipid composed of three fatty acids that are connected with ester. A lipid can be either a fat, steroids, cholesterol, or waxes..
Black Cat Brewery Lipids
These lipids belong to a heterogeneous class of predominantly nonpolar compounds,. Web what are the simplest forms (monomers) of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids? Web triglycerides are classified as simple lipids because they are formed from just two types of compounds: Web learn about types of lipids. They’re part of your cell membranes and help control what goes in.
The Summons Lab • Geobiology and Astrobiology at MIT » What is a biomarker?
The simplest lipid mixture shown to induce domain (“raft”) formation consists of cholesterol and both a saturated and unsaturated species of phospholipid. Hydrophilic (polar) phosphate heads 2. Web 7.2.3 lipid 7.2.3.1 triglyceride. Web a simple lipid is a fatty acid ester of different alcohols and carries no other substance. Web simple lipids are lipids that are formed when fatty acids.
Lipids Are Fatty Compounds That Perform A Variety Of Functions In Your Body.
Web lipid categorized into fatty acids and steroids. Web what are the simplest forms (monomers) of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids? Study examples of the classes of lipids, examine the structure and forms of lipids, and discover why lipids are important for. Lipids are not polymers but are macromolecules.
There Are Eight Categories Of Lipids Defined By The Lipid Maps.
Web a simple lipid is a fatty acid ester of different alcohols and carries no other substance. Web learn about types of lipids. Web simple lipids are lipids that are formed when fatty acids react with alcohols. Web lipid anabolism describes the production of complex lipid molecules from simple ones using energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (the energy source.
The Simplest Lipid Mixture Shown To Induce Domain (“Raft”) Formation Consists Of Cholesterol And Both A Saturated And Unsaturated Species Of Phospholipid.
Web lipids can form bonds to proteins and carbohydrates forming lipoproteins and lipopolysaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars and are the simplest form of. Triglyceride is the simplest lipid composed of three fatty acids that are connected with ester. Web triglycerides are classified as simple lipids because they are formed from just two types of compounds:
Web 7.2.3 Lipid 7.2.3.1 Triglyceride.
Web the simplest of these structures are micelles, spherical assemblies containing a hydrophobic interior of phospholipid tails and an outer surface of polar head groups. Hydrophilic (polar) phosphate heads 2. These lipids belong to a heterogeneous class of predominantly nonpolar compounds,. A lipid can be either a fat, steroids, cholesterol, or waxes.