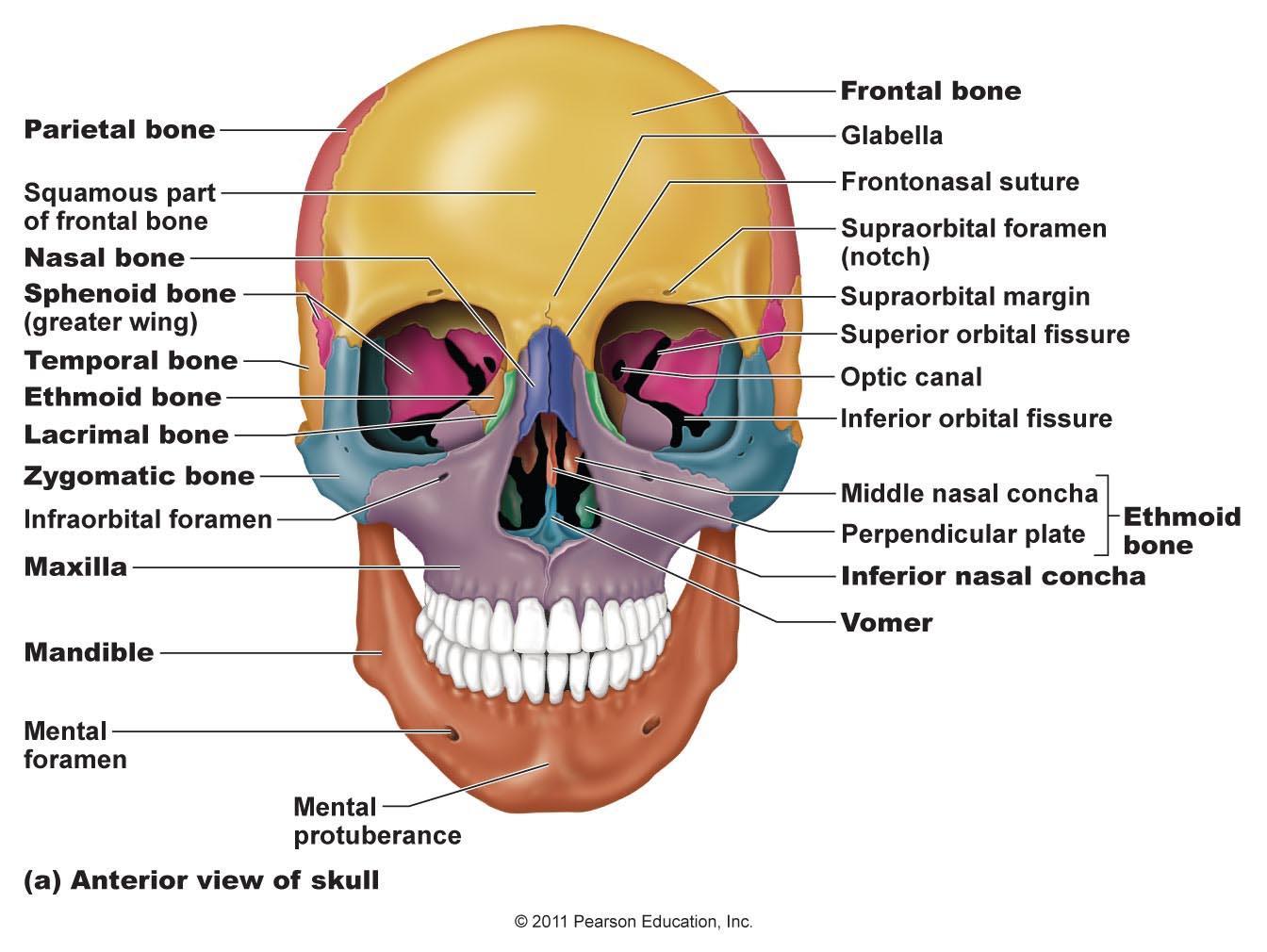
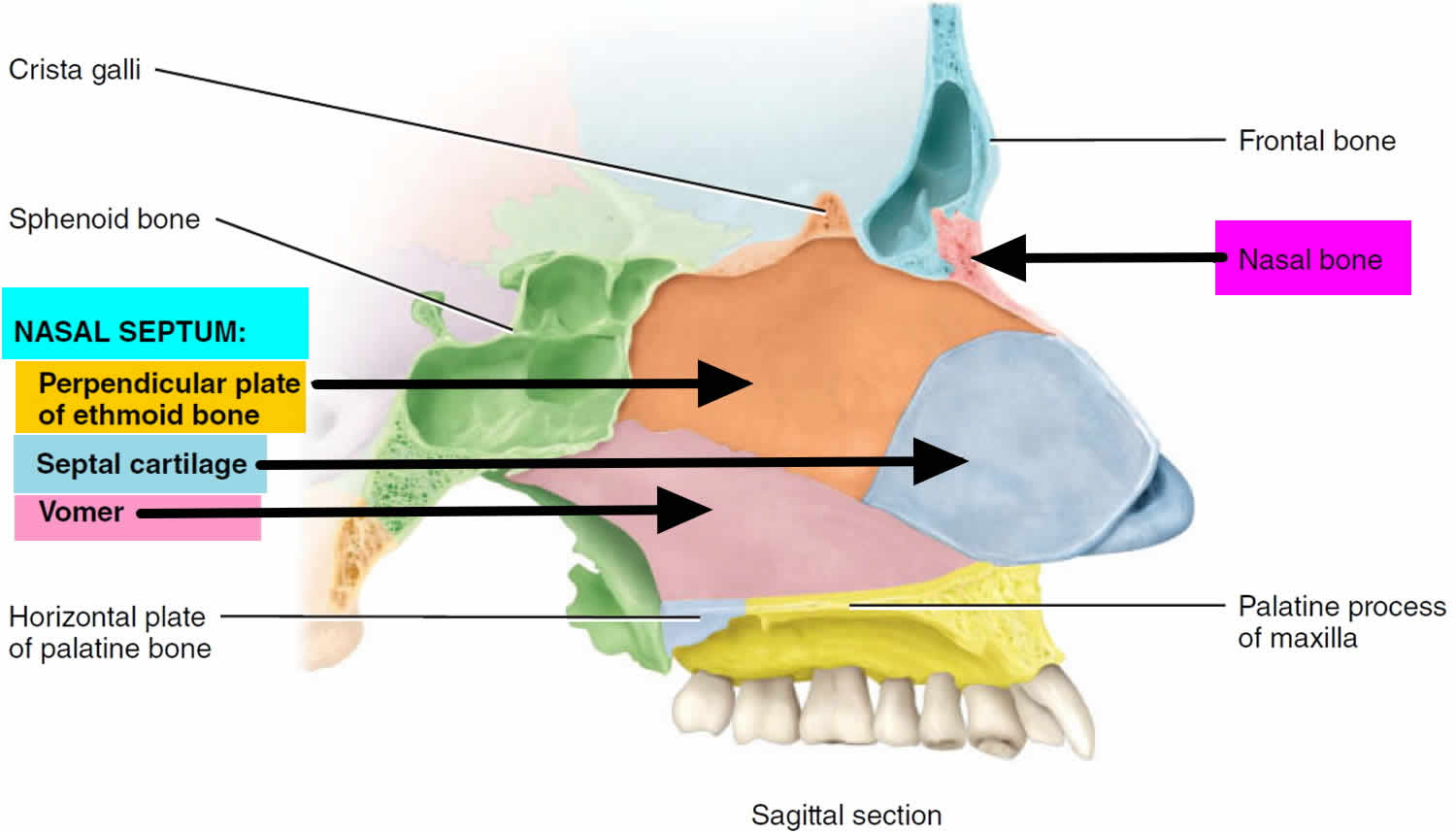
Which Bones Form The Nasal Septum
Which Bones Form The Nasal Septum - Connective tissue and skin cover the bony and cartilaginous components of the. The bones of the nose, forehead, sphenoid, and ethmoid are what make up the nose. Perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone, vomer bone, cartilage of the septum, crest of the maxillary bone, and crest of the palatine bone. Ethmoid and vomer which bone of the axial skeleton does not have a direct connection to any other bone? Each side of the nasal cavity is triangular in shape, with a broad inferior space that narrows superiorly. Web the posterior portion of the septum is made up of several different bones; Web how many bones are in the nasal septum? Web which bones make up the nasal septum, which divides the left nostril from the right? For others, a nose injury causes it. Crest of the palatine bone.
Web the bones that contribute to the nasal septum can be divided into: Web whilst the vomer, maxillary and palatine bones form the inferior part of the nasal septum 1). The bones contributing to the formation of the nasal septum can be classified as paired or unpaired. Each rectangular bone has an internal and external surface and four borders. The anterior portion is made of irregular quadrangular hyaline cartilage that inserts into the nasomaxillary crest of the maxilla and nasal spine. Nasal, maxillary and palatine bones unpaired bones: Where the maxilla and lacrimal bones connect, the lacrimal groove is formed. Web the external part of the nose consists of a root (superiorly), apex (inferiorly), dorsum, nares. The nasal septum is made up of cartilage and bone. Web the posterior portion of the septum is made up of several different bones;
The nasal septum is composed of five structures: A badly deviated septum may cause breathing problems, congestion and headaches. Web the nasal bone is a paired flat bone located at the upper third of the nose bridge. Crest of the maxillary bone. Web the posterior portion of the septum is made up of several different bones; Posteriorly it meets the concave anterior margins of the ethmoid and vomer. It runs down the center of your nose and separates the two nasal cavities. Each side of the nasal cavity is triangular in shape, with a broad inferior space that narrows superiorly. Connective tissue and skin cover the bony and cartilaginous components of the. These bones also feature holes (foramina) that allow veins to pass through from the skin.
Nasal Cavity arterial supply and nasal meatuses and chonchae
Each side of the nasal cavity is triangular in shape, with a broad inferior space that narrows superiorly. Nasal, maxillary and palatine bones unpaired bones: Web how many bones are in the nasal septum? It is made up of the septal cartilage, the vomer bone , and the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone. Web the nasal bone is a.
Vomer Bone In Nose The primary bone in the septum of the nose is
Anteriorly the septal cartilage (quadrangular cartilage) approximates a quadrilateral shape. These cells communicate with your brain to provide a sense of smell. Perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone. This groove is where the lacrimal sac resides. It makes up the facial skeleton ( viscerocranium) along with the zygomatic bone, maxillae, palatine bones, lacrimal bones, inferior nasal conchae, vomer and mandible.
Nasal Cavity Definition, Anatomy, Functions, Diagrams
When looking into the nasal cavity from the front of the skull, two bony plates are seen projecting from each lateral wall. The perpendicular plate of the ethmoid, the vomer (one discrete septal bone), both of which are tucked underneath the nasal bones. The roof of a building. Ethmoid and vomer which bone of the axial skeleton does not have.
Bones Forming Nasal Cavity Medial Wall Of The Nasal Cavity Anatomy
It makes up the facial skeleton ( viscerocranium) along with the zygomatic bone, maxillae, palatine bones, lacrimal bones, inferior nasal conchae, vomer and mandible. The perpendicular plate of the ethmoid, the vomer (one discrete septal bone), both of which are tucked underneath the nasal bones. The septum is made of bone and firm cartilage. Web the posterior portion of the.
Deviated Septum Causes, Symptoms, How To Fix A Deviated Septum
Web which bones form the roof of nasal cavity? The lacrimal sac is important in the tear production process. Web the upper portion of the nasal septum is formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone and the lower portion is the vomer bone. Web the fleshy external end of the nasal septum is sometimes also called columella. Anteriorly.
nasal complex bones Google Search Nasal septum, Nasal cavity
Nasal, maxillary, and palatine bones. Web the nasal septum is in the midline of the nose and made of flat cartilage anteriorly and bone posteriorly. Surgery can repair a deviated septum. The larger of these is the inferior nasal concha, an independent bone of the skull. Web os nasale 1/7 synonyms:
Anatomy of nasal septum. Download Scientific Diagram
These are the openings to the nasal cavities that are on the face. Maxillary bone (the crest) perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone; The bones of your nose are known as the nasal septum. These cells communicate with your brain to provide a sense of smell. Departure of the nasal septum from the center line of the nose.
Nasal septum anatomy, function, nasal septum deviation & hole
Is nasal septum a bone? Web the upper portion of the nasal septum is formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone and the lower portion is the vomer bone. Web which bones form the roof of nasal cavity? The nose is divided into two sides by the septum. For others, a nose injury causes it.
Pin on Learn Anatomy
Is nasal septum a bone? Web the upper portion of the nasal septum is formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone and the lower portion is the vomer bone. Web which bones form the roof of nasal cavity? The lowest part of the septum is a narrow strip of bone that projects from the maxilla. Web the bones.
Deviated Septum Causes, Symptoms, How To Fix A Deviated Septum
It makes up the facial skeleton ( viscerocranium) along with the zygomatic bone, maxillae, palatine bones, lacrimal bones, inferior nasal conchae, vomer and mandible. Each rectangular bone has an internal and external surface and four borders. The paired bones are the: Perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone. The nose is divided into two sides by the septum.
Web The Bones That Contribute To The Nasal Septum Can Be Divided Into:
Maxillary bone (the crest) perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone; It makes up the facial skeleton ( viscerocranium) along with the zygomatic bone, maxillae, palatine bones, lacrimal bones, inferior nasal conchae, vomer and mandible. For others, a nose injury causes it. Nasal, maxillary, and palatine bones.
Web The External Part Of The Nose Consists Of A Root (Superiorly), Apex (Inferiorly), Dorsum, Nares.
Web whilst the vomer, maxillary and palatine bones form the inferior part of the nasal septum 1). Ethmoid and vomer which bone of the axial skeleton does not have a direct connection to any other bone? Each rectangular bone has an internal and external surface and four borders. The quadrangular cartilage makes up the front part of the nasal septum, and the ethmoid and vomer bones make up the paper.
It Runs Down The Center Of Your Nose And Separates The Two Nasal Cavities.
Web the nasal bone is a paired flat bone located at the upper third of the nose bridge. The nasal septum contains bone and hyaline cartilage. Web nasal septum is composed of five structures: Web the posterior portion of the septum is made up of several different bones;
Departure Of The Nasal Septum From The Center Line Of The Nose.
Crest of the palatine bone. Web the nasal septum is in the midline of the nose and made of flat cartilage anteriorly and bone posteriorly. Some people are born with a deviated septum. The nasal septum is made up of cartilage and bone.